前言
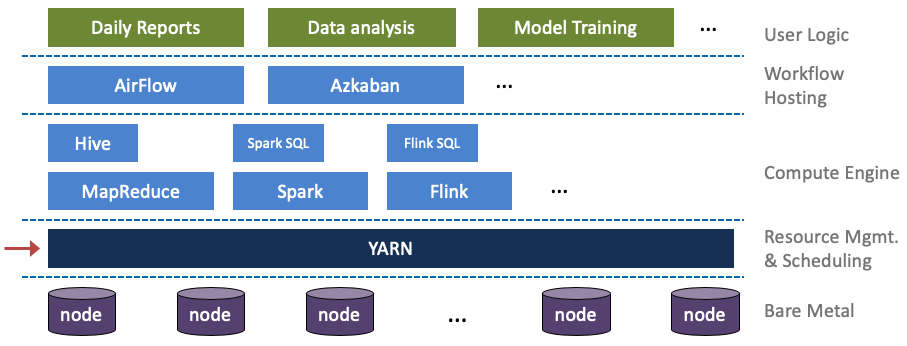
Yarn 的整体架构
Yarn 是 Hadoop2.x 版本提出的一种全新的资源管理架构,基于主从(Master-Slave)模式,主要由 ResourceManager(RM)和NodeManager(NM)两大部分组成。除此之外,还有 ApplicationMaster(AM)、Application Manager、Scheduler 及 Container 等组件辅助实现所有功能。
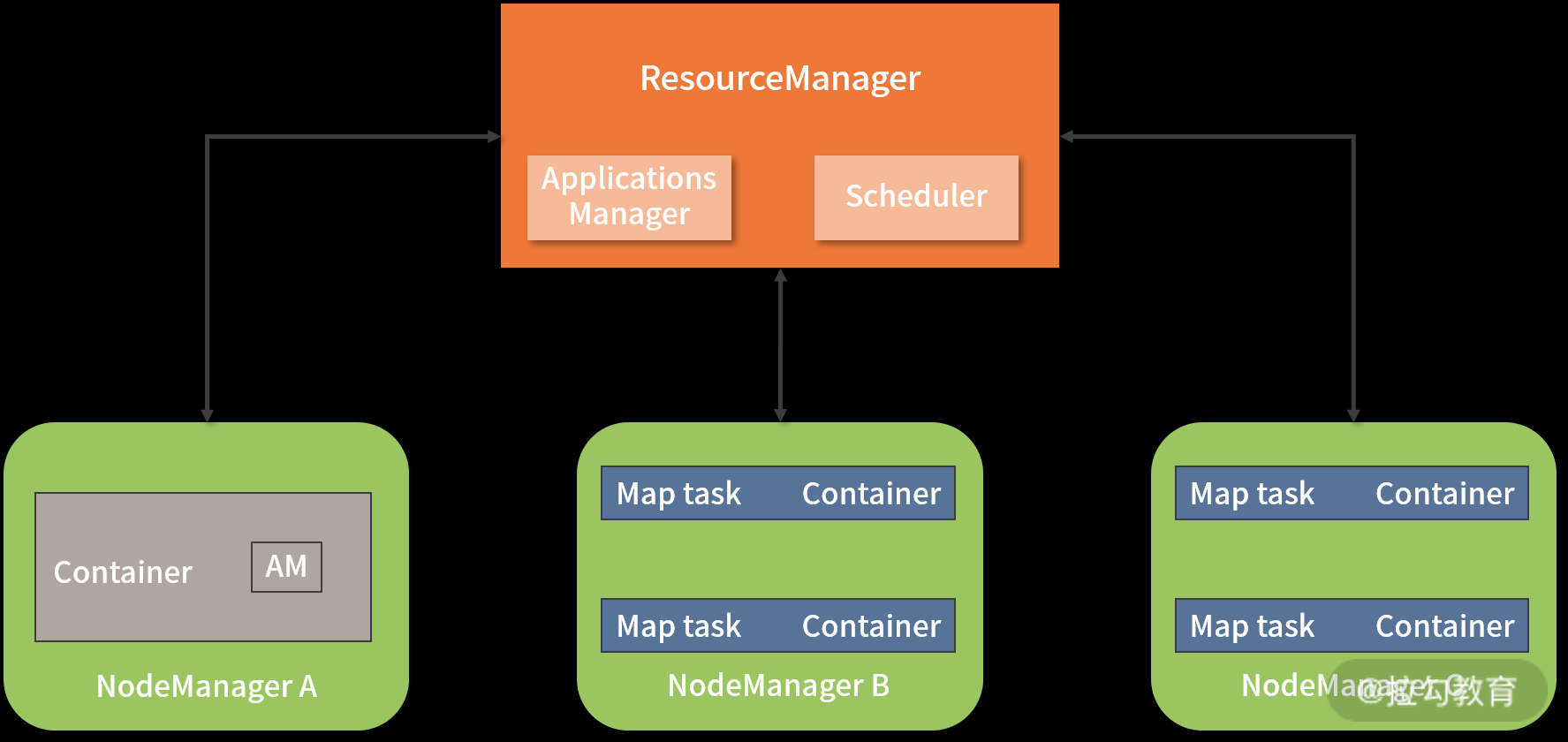
- RM 是一个全局的资源管理器,集群里只有一个。由两个组件组成
- ApplicationsManager 负责管理整个集群中所有的应用程序,包括应用程序的提交、与调度器协商资源、启动 ApplicationMaster、监控 ApplicationMaster 运行状态并在失败时重新启动它等。类似于k8s.controllerManager
- Scheduler 是一个纯粹的资源调度器,它只负责调度 Containers,不用关心任何与具体应用程序相关的工作。例如,它不会监控或者跟踪应用的执行状态,也不会去重启因程序失败或者其他错误而运行失败的任务。Yarn 提供了多种直接可用的调度器,常用的 Scheduler 主要有两种,即 Capacity Scheduler 和 Fair Scheduler。类似于k8s.scheduler
- ApplicationMaster 是应用程序级别的,当用户提交一个分析任务时,ApplicationMaster 进程首先启动。接着,它向 ResourceManager 申请资源并和 NodeManager 协同工作来运行此任务;同时,它还会跟踪监视任务的执行状态。当遇到失败的任务时自动重启它;当任务执行完成后,ApplicationMaster 会关闭自己并释放自己的容器。PS:类似于k8s的operator,但k8s的operator 是常驻的
- NodeManager 进程运行在集群中的多个计算节点上,负责每个节点上资源(CPU 和内存)的使用,处理来自ResourceManger/ApplicationMaster的命令 。类似于k8s的kubelet
Yarn 应用提交过程分析
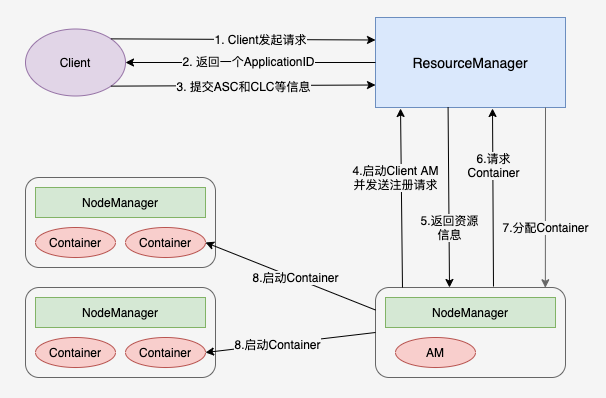
- 客户端向 RM 发出请求
- RM 返回一个 ApplicationID 作为回应
- 客户端向 RM 回应 Application Submission Context(ASC)和 Container Launch Context(CLC)信息。其中 ASC 包括 ApplicationID、user、queue,以及其它一些启动 AM 相关的信息,CLC 包含了资源请求数(内存与CPU),Job 文件,安全 token,以及其它一些用于在 NM 上启动 AM的信息;
- 当 ResourceManager 接受到 ASC 后,开启一个 Container,它会调度一个合适的 container 来启动 AM(经常被称做 container 0,mem=1.5G,core=1)
- 当 AM 启动起来后,RM 回应给 AM 集群的最小与最大资源等信息。这时 AM 必须决定如何使用那么当前可用的资源。Yarm 不像那些请求固定资源的 scheduler,它能够根据集群的当前状态动态调整;
- AM 根据从 RM 那里得知的可使用的资源,它会请求一些一定数目的 container。这个请求可以是非常具体的包括具有多个资源最小值的 Container(例如额外的内存等);
- RM 将会根据调度策略,尽可能的满足 AM 申请的 container;
- AM 根据分配的信息,去找NM启动对应的 container。
- 各个任务通过 RPC 协议向 ApplicationMaster 汇报自己的状态和进度,以此方式让ApplicationMaster 随时掌握各个任务的运行状态,从而可以在任务失败时重新启动任务;
- ApplicationMaster 将任务执行结果返回给 ApplicationManager,并在应用程序运行完成后向 ApplicationManager 注销并关闭自己。
源码分析
运行 Container 是由插拔式组件 ContainerExecutor 完成,Yarn 中提供了三种 ContainerExecutor 实现:DefaultContainerExecutor/ LinuxContainerExecutor/DockerContainerExecutor,DefaultContainerExecutor 实质是启动了 一个新的进程 java.lang.Process。
public class DefaultContainerExecutor extends ContainerExecutor {
@Override
public int launchContainer(ContainerStartContext ctx)throws IOException, ConfigurationException {
Container container = ctx.getContainer(); // container 在此处更多是一个资源概念,它的一些资源限制参数会在启动 进程时用到。
Path nmPrivateContainerScriptPath = ctx.getNmPrivateContainerScriptPath();
String user = ctx.getUser();
Path containerWorkDir = ctx.getContainerWorkDir();
// create container dirs on all disks
// Create the container log-dirs on all disks
// copy container tokens to work dir
// copy launch script to work dir
Path launchDst = new Path(containerWorkDir, ContainerLaunch.CONTAINER_SCRIPT);
copyFile(nmPrivateContainerScriptPath, launchDst, user);
// Create new local launch wrapper script
LocalWrapperScriptBuilder sb = getLocalWrapperScriptBuilder(containerIdStr, containerWorkDir);
Path pidFile = getPidFilePath(containerId);
sb.writeLocalWrapperScript(launchDst, pidFile);
// create log dir under app
// fork script
Shell.CommandExecutor shExec = null;
try {
setScriptExecutable(launchDst, user);
setScriptExecutable(sb.getWrapperScriptPath(), user);
shExec = buildCommandExecutor(sb.getWrapperScriptPath().toString(),containerIdStr, user, pidFile, container.getResource(),new File(containerWorkDir.toUri().getPath()),container.getLaunchContext().getEnvironment());
shExec.execute();
} catch (IOException e) {
} finally {
if (shExec != null) shExec.close();
}
return 0;
}
}
public static class ShellCommandExecutor extends Shell implements CommandExecutor {
public void execute() throws IOException {
this.run(); // ==> runCommand
}
private void runCommand() throws IOException {
ProcessBuilder builder = new ProcessBuilder(getExecString());
builder.environment().putAll(this.environment);
builder.directory(this.dir);
...
process = builder.start();
...
}
}
public final class ProcessBuilder{
public Process start() throws IOException {
return ProcessImpl.start(cmdarray,environment, dir,redirects,redirectErrorStream);
}
}
Yarn 中 shell 的使用
- Yarn application
- Yarn node
- Yarn queue
- Yarn rmadmin
- Yarn logs