简介
访问 k8s 集群获取资源有多种方式
- 命令行 kubectl
- http k8s REST API
- 代码库 client-go
- ClientSet
- Dynamic Client
- RESTClient
- informer
Kubernetes的client-go库介绍client-go是一个调用kubernetes集群资源对象http API的客户端(是一个典型的web服务客户端库),即通过client-go实现对kubernetes集群中资源对象(包括deployment、service、ingress、replicaSet、pod、namespace、node等)的增删改查等操作。
使用方式
包结构
k8s.io/client-go
/rest // 底层rest client 定义 RESTClient struct
/kubernetes // 访问 Kubernetes API的一系列的clientset
/typed
/core/v1
/pod.go // pod 相关api
/extensions/v1beta1
/deployment.go // deployment 相关api
/dynamic // 对任意Kubernetes对象执行通用操作的动态client
/dynamicinformer
/dynamiclister
/interface.go
/informer
k8s.io/api
/core/v1
/types.go // 定义了pod service 等struct
/register.go
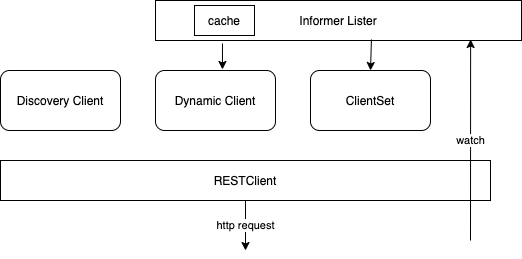
RESTClient
RESTClient是所有客户端的父类,底层调用了Go语言net\http库,访问API Server的RESTful接口。以查询pod 为例
// 从本机加载kubeconfig配置文件,因此第一个参数为空字符串
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", *kubeconfig)
config.APIPath = "api"
config.GroupVersion = &corev1.SchemeGroupVersion // schema.GroupVersion{Group: GroupName, Version: "v1"}
// 指定序列化工具
config.NegotiatedSerializer = scheme.Codecs
// 根据配置信息构建restClient实例
restClient, err := rest.RESTClientFor(config)
// 保存pod结果的数据结构实例
result := &corev1.PodList{}
// GET请求
err = restClient.Get().
// 指定namespace,参考path : /api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods
Namespace(namespace).
// 查找多个pod,参考path : /api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods
Resource("pods").
// 指定大小限制和序列化工具
VersionedParams(&metav1.ListOptions{Limit:100}, scheme.ParameterCodec).
// 请求
Do(context.TODO()).
// 结果存入result
Into(result)
ClientSet 方式
类似于 /core/v1 和 /extensions/v1beta1 这些GroupVersion 在 k8s.io/client-go 和 k8s.io/api 都有对应目录。
config,err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("",kubeconfig)
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
pod,err := clientset
.CoreV1() // 选择APIGroupVersion 即 /api/v1
.Pods("book") // 命名空间
.Get("example",metav1.GetOptions{}) // 访问 /api/v1/namespaces/book/pods/example
以node resource 为例,展示使用client-go 对 resource 进行查询和更新
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
// 获取node 列表
nodes, err := clientset.CoreV1().Nodes().List(context.TODO(), metav1.ListOptions{})
// 更新
_, err = a.client.CoreV1().Nodes().Update(context.TODO(), newNode, metav1.UpdateOptions{})
// 发送patch 指令更新
patchTemplate := map[string]interface{}{
"metadata": map[string]interface{}{
"labels": map[string]interface{}{
labelkey: labelvaule,
},
},
}
patchdata, _ := json.Marshal(patchTemplate)
_, err := clientset.CoreV1().Nodes().Patch(ctx, Nodes[i].Name, types.StrategicMergePatchType, patchdata, metav1.PatchOptions{})
给pod 添加label,有时直接Update 容器revision conflict
labelPatch := fmt.Sprintf(`[{"op":"add","path":"/metadata/labels/%s","value":"%s" }]`, "labelkey", "labelvaule")
_, err = sc.kubeClient.CoreV1().Pods(p.Namespace).Patch(context.TODO(), p.Name, types.JSONPatchType, []byte(labelPatch), metav1.PatchOptions{})
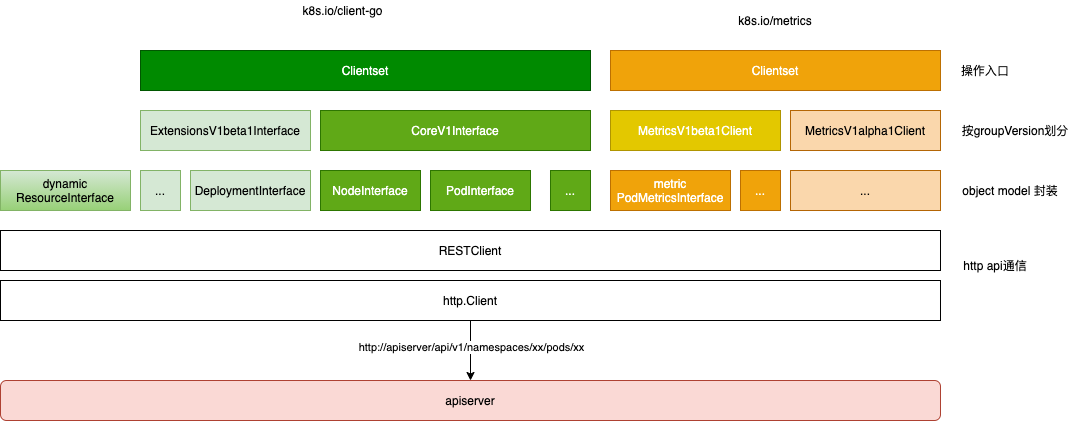
从上到下来说:Clientset是调用Kubernetes资源对象最常用的client,可以操作所有的资源对象。需要指定Group、Version,然后根据Resource获取 对应的XXInterface。
pod /node 等API Resource 按GroupVersion(CoreV1/ExtensionsV1beta1) 进行了聚合,对外提供CoreV1Client/ExtensionsV1beta1Client,各个GroupVersion Interface 聚合为 clientset
type CoreV1Interface interface {
RESTClient() rest.Interface
ConfigMapsGetter
EventsGetter
NamespacesGetter
NodesGetter
PersistentVolumesGetter
PersistentVolumeClaimsGetter
PodsGetter
PodTemplatesGetter
ReplicationControllersGetter
SecretsGetter
ServicesGetter
...
}
type CoreV1Client struct {
restClient rest.Interface // 通用的REST 客户端
}
以pod 为例,对外提供了 PodInterface 封装了对Pod 的api。 Pod 的schema 数据 k8s.io/api 对应GroupVesion 路径下的 register.go 文件中 注册到 统一的 Schema 中,schema 数据在client-go 中用于 http 数据的解封装。
// k8s.io/client-go/deprecated/typed/core/v1/pod.go
type PodInterface interface {
Create(*v1.Pod) (*v1.Pod, error)
Update(*v1.Pod) (*v1.Pod, error)
Delete(name string, options *metav1.DeleteOptions) error
Get(name string, options metav1.GetOptions) (*v1.Pod, error)
List(opts metav1.ListOptions) (*v1.PodList, error)
Watch(opts metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
Patch(name string, pt types.PatchType, data []byte, subresources ...string) (result *v1.Pod, err error)
...
}
// pods implements PodInterface
type pods struct {
client rest.Interface
ns string
}
// k8s.io/client-go/rest/client.go
type RESTClient struct {
base *url.URL
Client *http.Client
...
}
func (c *pods) Get(name string, options metav1.GetOptions) (result *v1.Pod, err error) {
result = &v1.Pod{}
err = c.client.Get(). // 新建Request 对象
Namespace(c.ns). // 设置Request.namespace
Resource("pods"). // 设置Request.resource
Name(name). // 设置Request.resourceName
VersionedParams(&options, scheme.ParameterCodec).
Do(context.TODO()). // 执行Request.request
Into(result)
return
}
client-go 包含了 k8s 一些核心对象的访问,此外一些非核心对象 或用户crd 对象可以独立提供类似 client-go 功能
- 比如metric 机制相关的 PodMetrics/NodeMetrics对象,其代码都在
k8s.io/metrics包里。 - controller-runtime 为cr 生成对应的client,scheme中 包含了cr 的信息。
informer 方式
“高冷”的 Kubernetes Informer 一探究竟为了让 Client-go 更快地返回 List/Get 请求的结果、减少对 Kubenetes API 的直接调用,Informer 被设计实现为一个依赖(并且只依赖) Kubernetes List/Watch API 、可监听事件并触发回调函数的二级缓存工具包。PS:这点zk/etcd 等client 也提供类似能力,只是zk/etcd client 存储的是通用数据,没有封装资源对象。
Informer是一个带有本地缓存和索引机制的、可以注册 EventHandler 的 client,本地缓存被称为 Store,索引被称为 Index。使用 informer 的目的是为了减轻 apiserver 数据交互的压力而抽象出来的一个 cache 层, 客户端对 apiserver 数据的 “读取” 和 “监听” 操作都通过本地 informer 进行(相对于直接监听apiserverresp, err := http.Get("http://apiserver:8080/api/v1/watch/pods?watch=yes"))。Informer 实例的Lister()方法可以直接查找缓存在本地内存中的数据。
// 通过informer 获取node 列表
factory := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(clientset, 30*time.Second)
nodeInformer := factory.Core().V1().Nodes()
go nodeInformer.Informer().Run(stopCh)
if !cache.WaitForCacheSync(stopCh, nodeInformer.Informer().HasSynced) {
runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Timed out waiting for caches to sync"))
return
}
nodes, err := nodeInformer.Lister().List(labels.NewSelector())
Dynamic client
Dynamic client 是一种动态的 client,它能处理 kubernetes 所有的资源。不同于 clientset,dynamic client 对GVK 一无所知, 返回的对象unstructured.Unstructured(在k8s.io/apimachinery 中定义,并注册到了schema 中) 是一个 map[string]interface{},如果一个 controller 中需要控制所有的 API,可以使用dynamic client,目前它在 garbage collector 和 namespace controller中被使用。
k8s.io/client-go
/dynamic
/dynamicinformer
/dynamiclister
/interface.go
dynamicClient, err := dynamic.NewForConfig(config)
gvr := schema.GroupVersionResource{Version: "v1", Resource: "pods"}
// 返回非结构化的对象
unstructObj, err := dynamicClient.Resource(gvr).Namespace("sandbox").List(context.TODO(), metav1.ListOptions{Limit: 40})
podList := corev1.PodList{}
// 额外做一次类型转换,如果这里传错类型,就会有类型安全的风险
err = runtime.DefaultUnstructuredConverter.FromUnstructured(unstructObj.UnstructuredContent(), podList)
相比底层的 RESTClient,基于 unstructured.Unstructured 实现了 数据的解封装 及watch 机制。
// k8s.io/client-go/dynamic/interface.go
type ResourceInterface interface {
Create(ctx context.Context, obj *unstructured.Unstructured, options metav1.CreateOptions, subresources ...string) (*unstructured.Unstructured, error)
Update(ctx context.Context, obj *unstructured.Unstructured, options metav1.UpdateOptions, subresources ...string) (*unstructured.Unstructured, error)
Delete(ctx context.Context, name string, options metav1.DeleteOptions, subresources ...string) error
Get(ctx context.Context, name string, options metav1.GetOptions, subresources ...string) (*unstructured.Unstructured, error)
List(ctx context.Context, opts metav1.ListOptions) (*unstructured.UnstructuredList, error)
Watch(ctx context.Context, opts metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
...
}
// k8s.io/client-go/dynamic/simple.go
func (c *dynamicResourceClient) Get(ctx context.Context, name string, opts metav1.GetOptions, subresources ...string) (*unstructured.Unstructured, error) {
// 这里直接拼接了 api resource 的请求路径
result := c.client.client.Get().AbsPath(append(c.makeURLSegments(name), subresources...)...).SpecificallyVersionedParams(&opts, dynamicParameterCodec, versionV1).Do(ctx)
retBytes, err := result.Raw()
uncastObj, err := runtime.Decode(unstructured.UnstructuredJSONScheme, retBytes)
return uncastObj.(*unstructured.Unstructured), nil
}
其它
首先说client之前,必须要先初始化一个config结构。
// k8s.io/client-go@v0.19.11/tools/clientcmd/client_config.go
func BuildConfigFromFlags(masterUrl, kubeconfigPath string) (*restclient.Config, error) {
if kubeconfigPath == "" && masterUrl == "" {
klog.Warningf("Neither --kubeconfig nor --master was specified. Using the inClusterConfig. This might not work.")
kubeconfig, err := restclient.InClusterConfig()
if err == nil {
return kubeconfig, nil
}
klog.Warning("error creating inClusterConfig, falling back to default config: ", err)
}
return NewNonInteractiveDeferredLoadingClientConfig(
&ClientConfigLoadingRules{ExplicitPath: kubeconfigPath},
&ConfigOverrides{ClusterInfo: clientcmdapi.Cluster{Server: masterUrl}}).ClientConfig()
}
- 如果在外部集群,可以读取kubeconfig作为配置(默认为
~/.kube/config); - 如果运行在集群中,可以采用serviceaccount 的方式,client-go从
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token和/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt读取文件,对应InClusterConfig
client-go 定义了一个 ClientConfig interface,包含DeferredLoadingClientConfig/DirectClientConfig/InClusterConfig 实现。 clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags(masterUrl,kubeconfigPath)读取k8s config 是有搜索顺序的,如果masterUrl/kubeconfigPath 都为空,则会返回InClusterConfig,否则返回DeferredLoadingClientConfig。
更新status
更新status,以Deployment 为例,/apis/apps/v1beta1/namespaces/${ns}/deployments/${name} 只能更新deployment 的 spec。/apis/apps/v1beta1/namespaces/${ns}/deployments/${name}/status 只能更新 deployment 的status。