简介
openkruise 面向自动化场景的 Kubernetes workload扩展controller,它是一组controller,可在应用程序工作负载管理上扩展和补充Kubernetes核心控制器。cloneset 在很多方面上借鉴了 statefulset ,只是没有 statefulset 的 ordinal 序号。
类似功能 的还有 Argo Rollouts Argo Rollouts is a Kubernetes controller and set of CRDs which provide advanced deployment capabilities such as blue-green, canary, canary analysis, experimentation, and progressive delivery features to Kubernetes.
CloneSet
CloneSet 控制器提供了高效管理无状态应用的能力,一个简单的 CloneSet yaml 文件如下:
apiVersion: apps.kruise.io/v1alpha1
kind: CloneSet
metadata:
labels:
app: sample
name: sample
spec:
replicas: 5
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sample
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sample
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:alpine
spec.template 中定义了当前 CloneSet 中最新的 Pod 模板。 控制器会为每次更新过的 spec.template 计算一个 revision hash 值。在运行过程中,还会额外 为cloneset 管理的pod 加上 label=controller-revision-hash 标记pod 所属的revision。
运行后,describe cloneset 示例:
Name: sample
Namespace: default
Labels: app=sample
Annotations: API Version: apps.kruise.io/v1alpha1
Kind: CloneSet
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2020-08-17T09:39:08Z
Generation: 1
Resource Version: 307518
Self Link: /apis/apps.kruise.io/v1alpha1/namespaces/default/clonesets/sample
UID: 65534592-a998-4374-a2c7-56eeb1dd273b
Spec:
...
Status:
Available Replicas: 5
Collision Count: 0
Label Selector: app=sample
Observed Generation: 1
Ready Replicas: 5
Replicas: 5
Update Revision: sample-5cdbb7d879
Updated Ready Replicas: 5
Updated Replicas: 5
原地升级nginx pod 的status 示例
Labels: app=sample
apps.kruise.io/cloneset-instance-id=75v7q
controller-revision-hash=sample-549647c4b4
Annotations: inplace-update-state:
{"revision":"sample-549647c4b4","updateTimestamp":"2020-08-14T11:04:25Z","lastContainerStatuses":...}
Controlled By: CloneSet/sample
Status: Running // Pending/Running/Succeeded/Failed/Unknown
Readiness Gates:
Type Status
InPlaceUpdateReady True // 原地升级添加的自定义Readiness Gates
Conditions:
Type Status
InPlaceUpdateReady True
Initialized True // 所有的 Init 容器 都已成功启动
Ready False // Pod 可以为请求提供服务,并且应该被添加到对应服务的负载均衡池中
ContainersReady False // Pod 中所有容器都已就绪
PodScheduled True // Pod 已经被调度到某节点
CloneSet可以对标原生的 Deployment,但 CloneSet 提供了很多增强功能,比如扩缩容时删除特定pod,尤其提供了丰富的升级策略。
spec:
// 升级功能
updateStrategy:
type: // 升级方式,默认为重建升级ReCreate,支持尽可能原地升级InPlaceIfPossible 和 只能原地升级InPlaceOnly
inPlaceUpdateStrategy: // 原地升级策略,比如graceful period 等
partition: // Partition 的语义是 保留旧版本 Pod 的数量,默认为 0。 如果在发布过程中设置了 partition,则控制器只会将 (replicas - partition) 数量的 Pod 更新到最新版本。
MaxUnavailable: // 最大不可用的Pod数量,是一个绝对值或百分比
MaxSurge: // 最大弹性数量,即最多能扩出来超过 replicas 的 Pod 数量,是一个绝对值或百分比。
priorityStrategy: // 优先级策略,升级顺序相关
...
scatterStrategy: // 打散策略,升级顺序相关
paused: // 为true时发布暂停
PreUpdate: // 升级前钩子函数
PostUpdate: // 升级后钩子函数
// 扩缩容功能
scaleStrategy:
podsToDelete: // 允许用户在缩小 replicas 数量的同时,指定想要删除的 Pod 名字
CloneSet status 中的字段说明:
- status.replicas: Pod 总数
- status.readyReplicas: ready Pod 数量
- status.availableReplicas: ready and available Pod 数量 (满足 minReadySeconds)
- status.updateRevision: 最新版本的 revision hash 值
- status.updatedReplicas: 最新版本的 Pod 数量
- status.updatedReadyReplicas: 最新版本的 ready Pod 数量
Partition 的语义是保留旧版本 Pod 的数量或百分比。比如说一个 100 个副本的 CloneSet,在升级镜像时将 partition 数值阶段性改为 80 -> 60 -> 40 -> 20 -> 0,则完成了分 5 批次发布。在灰度发布的过程中,只需要前后调节 partition 数值,就能灵活得控制新旧版本的比例数量。CloneSet 所依据的 “新旧版本” 对应的是其 status 中的 updateRevision 和 currentRevision。 cloneset作者提到:cloneset partition其实是继承了原生 statefulset 的 partition 理念,只是没有 statefulset 的 ordinal 序号。Partition 的语义是 保留旧版本 Pod 的数量,笔者曾觉得有点违反直觉。但如果 partition 来表示新版本数量的话,每次全量发布、扩容时都应同步设置partition 的值(与replicas保持一致),partition 的默认值就不能是0 或不填了。
Reconcile 逻辑
在kubebuilder 把Controller 控制器模型 的代码 都自动生成之后,不同Controller 之间的逻辑差异便只剩下 Reconcile 了
整体逻辑
背景知识
- CloneSet Owned 三个资源:ControllerRevision、Pod、PVC。
- 控制器会为每次更新过的 spec.template 计算一个 revision hash 值并上报到 CloneSet status 中
- 比如上文中提到的 nginx,在创建之初拥有的第一个 template 版本,会创建一个对应的 ControllerRevision。而当修改了 image 版本之后,CloneSet Controller 会创建一个新的 ControllerRevision,可以理解为每一个 ControllerRevision 对应了每一个版本的 Template,也对应了每一个版本的 ControllerRevision hash。通过ControllerRevision,CloneSet 可以很方便地管理不同版本的 template 模板,还原 CloneSet。
- Pod label 中定义的 ControllerRevision hash(label name = “controller-revision-hash”),就是 ControllerRevision 的名字
// kruise/pkg/controller/cloneset/cloneset_controller.go
func (r *ReconcileCloneSet) Reconcile(request reconcile.Request) (reconcile.Result, error) {
// ReconcileCloneSet.reconcileFunc = ReconcileCloneSet.doReconcile
return r.reconcileFunc(request)
}
func (r *ReconcileCloneSet) doReconcile(request reconcile.Request) (res reconcile.Result, retErr error) {
startTime := time.Now()
// Fetch the CloneSet instance
instance := &appsv1alpha1.CloneSet{}
err := r.Get(context.TODO(), request.NamespacedName, instance)
coreControl := clonesetcore.New(instance)
selector, err := metav1.LabelSelectorAsSelector(instance.Spec.Selector)
// list all active Pods and PVCs belongs to cs
filteredPods, filteredPVCs, err := r.getOwnedResource(instance)
//release Pods ownerRef
filteredPods, err = r.claimPods(instance, filteredPods)
// list all revisions and sort them
revisions, err := r.controllerHistory.ListControllerRevisions(instance, selector)
// 排序规则 byRevision.Less 优先根据 CreationTimestamp排序 其次根据Name
history.SortControllerRevisions(revisions)
// get the current, and update revisions
currentRevision, updateRevision, collisionCount, err := r.getActiveRevisions(instance, revisions, clonesetutils.GetPodsRevisions(filteredPods))
newStatus := appsv1alpha1.CloneSetStatus{
ObservedGeneration: instance.Generation,
CurrentRevision: currentRevision.Name,
UpdateRevision: updateRevision.Name,
CollisionCount: new(int32),
LabelSelector: selector.String(),
}
*newStatus.CollisionCount = collisionCount
// scale and update pods
delayDuration, syncErr := r.syncCloneSet(instance, &newStatus, currentRevision, updateRevision, revisions, filteredPods, filteredPVCs)
// update new status
if err = r.statusUpdater.UpdateCloneSetStatus(instance, &newStatus, filteredPods); err != nil {
return reconcile.Result{}, err
}
if err = r.truncatePodsToDelete(instance, filteredPods); err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Failed to truncate podsToDelete for %s: %v", request, err)
}
if err = r.truncateHistory(instance, filteredPods, revisions, currentRevision, updateRevision); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to truncate history for %s: %v", request, err)
}
...
return reconcile.Result{RequeueAfter: delayDuration}, syncErr
}
扩缩容
syncCloneSet 根据 cloneSet 期望状态( 由replicas 以及updateStrategy描述 )以及pod的真实状态, 执行scale 或 update 逻辑
- scale逻辑 对应 scale.Interface:
- 需要做扩容或缩容的时候(也就是pod 实际数量不等于 replicas时),scale 通过 删除或创建特定Revision的pod 使得 新旧Revision pod 的数量符合replicas/partition/MaxSurge/maxUnavailable 要求
- 如果 pod 实际数量等于 replicas,scale 并不会进行处理,本次syncCloneSet 主要执行 update 逻辑。
- update逻辑对应 update.Interface:找到不符合 updateRevision 的pod,根据 partition/MaxSurge/maxUnavailable 以及pod 的ready 情况,计算需要更新的pod 的数量needToUpdateCount,从排序好的 pod 中选取 needToUpdateCount 个pod 执行更新逻辑。PS:选择该删的删掉,之后创建
- 如果配置了原地升级策略, 原地升级pod
- 如果是默认ReCreate 策略,按序删除pod
// kruise/pkg/controller/cloneset/cloneset_controller.go
func (r *ReconcileCloneSet) syncCloneSet(
instance *appsv1alpha1.CloneSet, newStatus *appsv1alpha1.CloneSetStatus,
currentRevision, updateRevision *apps.ControllerRevision, revisions []*apps.ControllerRevision,
filteredPods []*v1.Pod, filteredPVCs []*v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
) (time.Duration, error) {
// 根据 ControllerRevision 还原CloneSet
currentSet, err := r.revisionControl.ApplyRevision(instance, currentRevision)
updateSet, err := r.revisionControl.ApplyRevision(instance, updateRevision)
scaling, podsScaleErr = r.scaleControl.Manage(currentSet, updateSet, currentRevision.Name, updateRevision.Name, filteredPods, filteredPVCs)
if scaling {
return delayDuration, podsScaleErr
}
delayDuration, podsUpdateErr = r.updateControl.Manage(updateSet, updateRevision, revisions, filteredPods, filteredPVCs)
return delayDuration, err
}
扩容逻辑:如果发布的时候设置了 maxSurge,控制器会先多扩出来 maxSurge 数量的 Pod(此时 Pod 总数为 (replicas+maxSurge)),然后再开始发布存量的 Pod。 然后,当新版本 Pod 数量已经满足 replicas - partition 要求之后,控制器会再把多余的 maxSurge 数量的 Pod 删除掉,保证最终的 Pod 数量符合 replicas。此外,maxSurge 还受 升级方式(type)的影响:maxSurge 不允许配合 InPlaceOnly 更新模式使用(可以认为此时maxSurge=0?)。 另外,如果是与 InPlaceIfPossible 策略配合使用,控制器会先扩出来 maxSurge 数量的 Pod,再对存量 Pod 做原地升级。
// kruise/pkg/controller/cloneset/scale/cloneset_scale.go
func (r *realControl) Manage(
currentCS, updateCS *appsv1alpha1.CloneSet,
currentRevision, updateRevision string,
pods []*v1.Pod, pvcs []*v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
) (bool, error) {
// 获取 podsToDelete 中指定的pod
if podsToDelete := getPodsToDelete(updateCS, pods); len(podsToDelete) > 0 {
return r.deletePods(updateCS, podsToDelete, pvcs)
}
// 符合 updateRevision 的pod 为 updatedPods ,不符合的为notUpdatedPods
updatedPods, notUpdatedPods := clonesetutils.SplitPodsByRevision(pods, updateRevision)
// 一个CloneSet 最多允许(replicas + MaxSurge)个pod 存在,如果实际pod 小于这个数量(diff<0)则需要创建pod,否则(diff>0) 删除pod。
// diff 标记pod 总量是否ready;currentRevDiff 表示 currentRev 总量是否ready
diff, currentRevDiff := calculateDiffs(updateCS, updateRevision == currentRevision, len(pods), len(notUpdatedPods))
if diff < 0 {
// total number of this creation
expectedCreations := diff * -1
// lack number of current version
expectedCurrentCreations := 0
if currentRevDiff < 0 {
expectedCurrentCreations = currentRevDiff * -1
}
// available instance-id come from free pvc
availableIDs := getOrGenAvailableIDs(expectedCreations, pods, pvcs)
// pod 数量不足,就要创建expectedCreations 个pod,创建时需指明 currentRevision和updateRevision 的pod 分别创建几个
return r.createPods(expectedCreations, expectedCurrentCreations,
currentCS, updateCS, currentRevision, updateRevision, availableIDs.List(), existingPVCNames)
} else if diff > 0 {
// pod 数量较多 则选择 多余的 新老Revision pod 删除
podsToDelete := choosePodsToDelete(diff, currentRevDiff, notUpdatedPods, updatedPods)
return r.deletePods(updateCS, podsToDelete, pvcs)
}
// 如果diff = 0 什么都不做
return false, nil
}
更新逻辑
// 处理 升级间隔,计算真正需要 更新的pod
// kruise/pkg/controller/cloneset/update/cloneset_update.go
func (c *realControl) Manage(cs *appsv1alpha1.CloneSet,
updateRevision *apps.ControllerRevision, revisions []*apps.ControllerRevision,
pods []*v1.Pod, pvcs []*v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
) (time.Duration, error) {
// 1. find currently updated and not-ready count and all pods waiting to update
var waitUpdateIndexes []int
for i := range pods {
// 支持 在pod 上设置一些注解,控制升级间隔,比如inplace-update-grace,如果距离上一次pod 的grace period 还未到,则先放弃本次升级
// 如果pod 的revision 不是最新的revision ,则加入到waitUpdateIndexes
if clonesetutils.GetPodRevision(pods[i]) != updateRevision.Name {
waitUpdateIndexes = append(waitUpdateIndexes, i)
}
}
// 2. sort all pods waiting to update 排序规则ActivePods.Less , 越新的 pod 越靠前
// 3. 根据 replicas/partition/MaxSurge/maxUnavailable 以及pod Status(比如not ready)等 calculate max count of pods can update
needToUpdateCount := calculateUpdateCount(coreControl, cs.Spec.UpdateStrategy, cs.Spec.MinReadySeconds, int(*cs.Spec.Replicas), waitUpdateIndexes, pods)
if needToUpdateCount < len(waitUpdateIndexes) {
waitUpdateIndexes = waitUpdateIndexes[:needToUpdateCount]
}
// 4. update pods
for _, idx := range waitUpdateIndexes {
pod := pods[idx]
if duration, err := c.updatePod(cs, coreControl, updateRevision, revisions, pod, pvcs); err != nil {...}
}
return requeueDuration.Get(), nil
}
// 根据CloneSet 升级策略,执行升级逻辑
func (c *realControl) updatePod(cs *appsv1alpha1.CloneSet, coreControl clonesetcore.Control,
updateRevision *apps.ControllerRevision, revisions []*apps.ControllerRevision,
pod *v1.Pod, pvcs []*v1.PersistentVolumeClaim,
) (time.Duration, error) {
// 如果clone set 升级策略为 (尽量)原地升级,则进入原地升级流程
if cs.Spec.UpdateStrategy.Type == appsv1alpha1.InPlaceIfPossibleCloneSetUpdateStrategyType ||
cs.Spec.UpdateStrategy.Type == appsv1alpha1.InPlaceOnlyCloneSetUpdateStrategyType {
var oldRevision *apps.ControllerRevision
for _, r := range revisions {
if r.Name == clonesetutils.GetPodRevision(pod) {
oldRevision = r
break
}
}
res := c.inplaceControl.Update(pod, oldRevision, updateRevision, coreControl.GetUpdateOptions())
...
return ...
}
// 如果不是原地升级,则本次Reconcile 删除pod,待下次Reconcile 扩容时创建pod
if err := c.Delete(context.TODO(), pod); err != nil {
return 0, err
}
// handle pvc
return 0, nil
}
虽然 spec.updateStrategy.partition 指定了旧版的数量。但 update 逻辑的主要目的是 更新 (replicas - partition) 个 updateRevision 实例。如果连续多次灰度发布,则旧版 可能存在多个 revision(也就是说不是最新的revision 都是旧版,旧版不都是某一个revision),整个cloneset 可能存在2个以上 revision的 pod。 这与直觉上的 多版本pod管理 还是不一样的
高级特性
原地升级
如何为 Kubernetes 实现原地升级? 如何在Kubernetes中实现容器原地升级一个Pod中可能包含了主业务容器,还有不可剥离的依赖业务容器,以及SideCar组件容器等,如果因为要更新其中一个SideCar Container而继续按照ReCreate Pod的方式进行整个Pod的重建,那负担还是很大的。更新一个轻量的SideCar却导致了分钟级的单个Pod的重建过程,因此,我们迫切希望能实现,只升级Pod中的某个Container,而不用重建整个Pod。
Kubernetes把容器原地升级的能力只做在Kubelet这一层,并没有暴露在Deployment、StatefulSet等Controller中直接提供给用户,原因很简单,还是建议大家把Pod作为完整的部署单元。为了实现容器原地升级,我们更改Pod.Spec中对应容器的Image,就会生成kubetypes.UPDATE类型的事件,kubelet 将容器优雅终止。旧的容器被杀死之后,kubelet启动新的容器,如此即完成Pod不重建的前提下实现容器的原地升级。
不过这样可能存在的几个风险:
- 容器 升级时 有一段时间服务不可用,但k8s 组件 无法感知,这用到了 readinessGatesYour application can inject extra feedback or signals into PodStatus: Pod readiness. To use this, set readinessGates in the Pod’s spec to specify a list of additional conditions that the kubelet evaluates for Pod readiness.Readiness gates are determined by the current state of status.condition fields for the Pod. If Kubernetes cannot find such a condition in the status.conditions field of a Pod, the status of the condition is defaulted to “False”. 当一个 Pod 被原地升级时,控制器会先利用 readinessGates 把 Pod status 中修改为 not-ready 状态,然后再更新 Pod spec 中的 image 字段来触发 Kubelet 重建对应的容器。
- 有时候 Kubelet 重建容器太快,还没等到其他控制器如 endpoints-controller 感知到 Pod not-ready,可能会导致流量受损。因此又在原地升级中提供了 graceful period 选项,作为优雅原地升级的策略。用户如果配置了 gracePeriodSeconds 这个字段,控制器在原地升级的过程中会先把 Pod status 改为 not-ready,然后等一段时间(gracePeriodSeconds),最后再去修改 Pod spec 中的镜像版本。 这样,就为 endpoints-controller 这些控制器留出了充足的时间来将 Pod 从 endpoints 端点列表中去除。
// kruise/pkg/util/inplaceupdate/inplace_utils.go
func (c *realControl) Update(pod *v1.Pod, oldRevision, newRevision *apps.ControllerRevision, opts *UpdateOptions) UpdateResult {
// 1. calculate inplace update spec
var spec *UpdateSpec
if opts == nil || opts.CustomizeSpecCalculate == nil {
// 只对更新了 spec.containers[x].image 的pod 进行原地升级
spec = calculateInPlaceUpdateSpec(oldRevision, newRevision)
}
if opts != nil && opts.GracePeriodSeconds > 0 {
spec.GraceSeconds = opts.GracePeriodSeconds
}
// 2. update condition for pod with readiness-gate
if containsReadinessGate(pod) {
newCondition := v1.PodCondition{
Type: appsv1alpha1.InPlaceUpdateReady,
LastTransitionTime: c.now(),
Status: v1.ConditionFalse,
Reason: "StartInPlaceUpdate",
}
if err := c.updateCondition(pod, newCondition); err != nil {
return UpdateResult{InPlaceUpdate: true, UpdateErr: err}
}
}
// 3. update container images
if err := c.updatePodInPlace(pod, spec, opts); err != nil {
return UpdateResult{InPlaceUpdate: true, UpdateErr: err}
}
...
}
func (c *realControl) updatePodInPlace(pod *v1.Pod, spec *UpdateSpec, opts *UpdateOptions) error {
return retry.RetryOnConflict(retry.DefaultBackoff, func() error {
clone, err := c.adp.getPod(pod.Namespace, pod.Name)
// update new revision 给pod 加上revision label
if c.revisionKey != "" {
clone.Labels[c.revisionKey] = spec.Revision
}
// record old containerStatuses
inPlaceUpdateStateJSON, _ := json.Marshal(inPlaceUpdateState)
clone.Annotations[appsv1alpha1.InPlaceUpdateStateKey] = string(inPlaceUpdateStateJSON)
if spec.GraceSeconds <= 0 {
if clone, err = patchUpdateSpecToPod(clone, spec, opts); err != nil {
return err
}
delete(clone.Annotations, appsv1alpha1.InPlaceUpdateGraceKey)
} else {
inPlaceUpdateSpecJSON, _ := json.Marshal(spec)
clone.Annotations[appsv1alpha1.InPlaceUpdateGraceKey] = string(inPlaceUpdateSpecJSON)
}
// 使用k8s api 更新pod
return c.adp.updatePod(clone)
})
}
计算待更新pod 的spec ,condition,container status 等数据, 加上revision label, inplace-update-grace annotation ,最终使用k8s api 更新pod 到k8s cluster
协程间同步状态
事件一直在产生 并由不同的协程处理, 如果一个协程正在对cloneset 做扩容操作,那么另一个协程需要等待一下,所以需要一个协程间的协调机制。
type ScaleExpectations interface {
ExpectScale(controllerKey string, action ScaleAction, name string)
ObserveScale(controllerKey string, action ScaleAction, name string)
SatisfiedExpectations(controllerKey string) (bool, time.Duration, map[ScaleAction][]string)
DeleteExpectations(controllerKey string)
GetExpectations(controllerKey string) map[ScaleAction]sets.String
}
type realScaleExpectations struct {
sync.Mutex
// key: parent key, workload namespace/name
controllerCache map[string]*realControllerScaleExpectations
}
一个协程进行某操作前先 ExpectScale,操作完成后再ObserveScale,另一个协程可以通过 SatisfiedExpectations 来检查 操作是否完成。
// github.com/openkruise/kruise/pkg/controller/cloneset/scale/cloneset_scale.go
func (r *realControl) createPods(...){
// 先ExpectScale
for _, p := range newPods {
clonesetutils.ScaleExpectations.ExpectScale(clonesetutils.GetControllerKey(updateCS), expectations.Create, p.Name)
podsCreationChan <- p
}
// 创建pod 逻辑
...
// 完成后 ObserveScale
for _, pod := range newPods {
if _, ok := successPodNames.Load(pod.Name); !ok {
clonesetutils.ScaleExpectations.ObserveScale(clonesetutils.GetControllerKey(updateCS), expectations.Create, pod.Name)
}
}
}
// github.com/openkruise/kruise/pkg/controller/cloneset/cloneset_controller.go
func (r *ReconcileCloneSet) doReconcile(request reconcile.Request) (res reconcile.Result, retErr error) {
...
// 另一个协程做检测
if scaleSatisfied, unsatisfiedDuration, scaleDirtyPods := clonesetutils.ScaleExpectations.SatisfiedExpectations(request.String()); !scaleSatisfied {
if unsatisfiedDuration >= expectations.ExpectationTimeout {
klog.Warningf("Expectation unsatisfied overtime for %v, scaleDirtyPods=%v, overtime=%v", request.String(), scaleDirtyPods, unsatisfiedDuration)
return reconcile.Result{}, nil
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Not satisfied scale for %v, scaleDirtyPods=%v", request.String(), scaleDirtyPods)
return reconcile.Result{RequeueAfter: expectations.ExpectationTimeout - unsatisfiedDuration}, nil
}
...
}
通过操作pod 来影响cloneset的策略
apiVersion: apps.kruise.io/v1alpha1
kind: CloneSet
spec:
# ...
updateStrategy:
priorityStrategy:
weightPriority:
- weight: 50
matchSelector:
matchLabels:
test-key: foo
- weight: 30
matchSelector:
matchLabels:
test-key: bar
在操作cloneset 发布之前,为pod 打上label,则test-key=foo 会比test-key= bar的pod 先升级。
CloneSet管理的Pod有以下状态 • Normal:正常状态 • PreparingUpdate: 准备原地升级 • Updating: 原地升级中 • Updated:原地升级完成 • PreparingDelete:准备删除
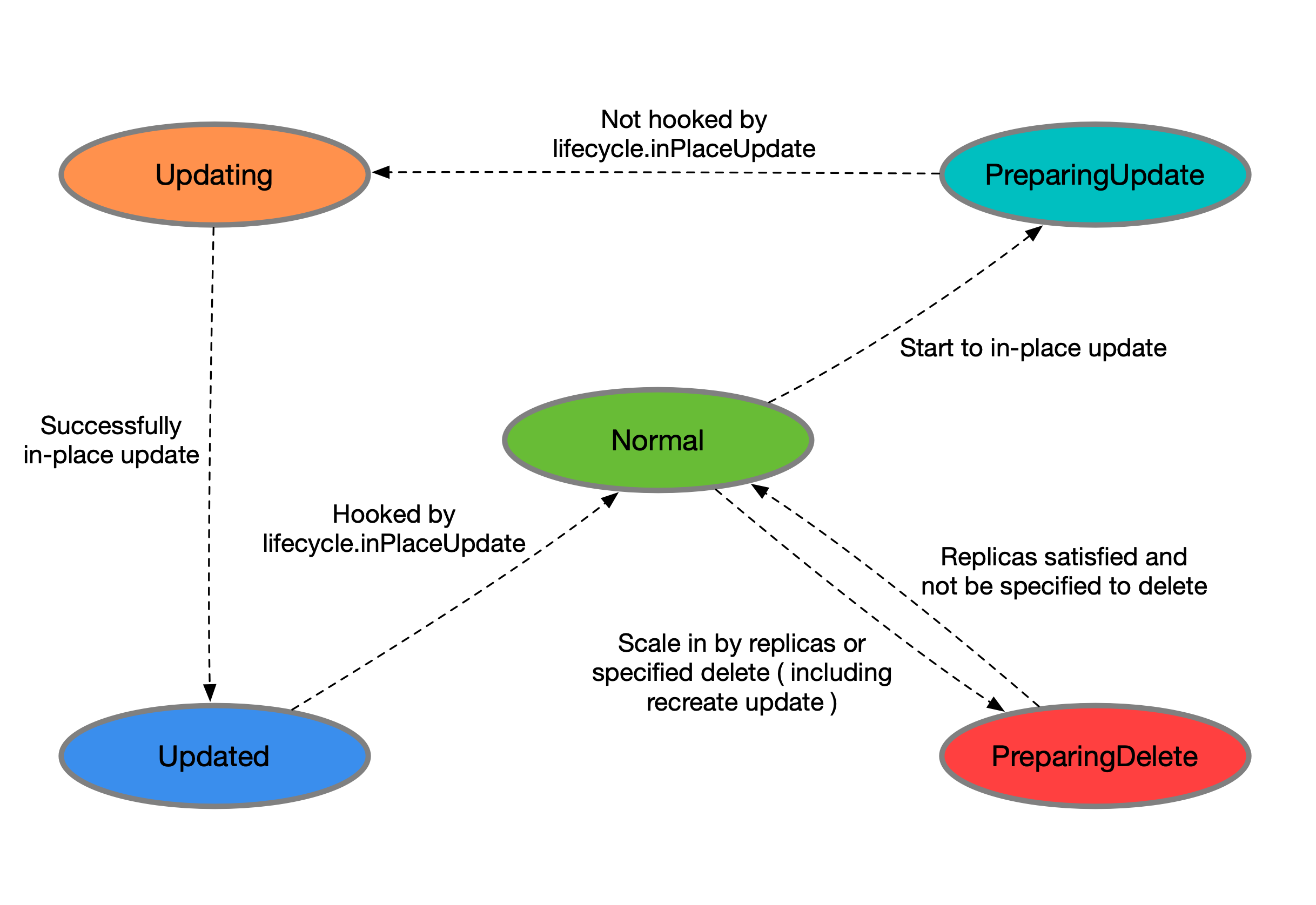
apiVersion: apps.kruise.io/v1alpha1
kind: CloneSet
spec:
# 通过 finalizer 定义 hook
lifecycle:
preDelete:
finalizersHandler:
- example.io/unready-blocker
inPlaceUpdate:
finalizersHandler:
- example.io/unready-blocker
# 或者也可以通过 label 定义
lifecycle:
inPlaceUpdate:
labelsHandler:
example.io/block-unready: "true"
如果定义了 lifecycle hook /preDelete,cloneset先只将 Pod 状态改为 PreparingDelete,当开发移除 label/finalizer后,kruise 才执行 Pod 删除,否则会直接删除pod。PS:也就是说,如果没有定义lifecycle hook /preDelete,pod 是没有PreparingDelete 状态的。