简介
基本思路
”有则返回,无则查db“的基本思路,有点像缺页中断,伪代码如下
cache.get(key){
value = loadFromCache(key);
if(null != value){
return value;
}
value = loader.load(key);
}
loader.load(key){
// 此处是竞争点,得有线程安全保护,线程发现有其它线程在查询key时,放弃执行,直接等待结果
value = loadFromDB(key);
storeToCache(value);
}
// 增强版本
loader.load(key){
// map<key,future> futureMap
Future future = futureMap.get(key);
if(null != future){
value = loadFromDB(key);
storeToCache(value);
}{
future.get();
}
}
从外向内

Cache的核心是LocalCache
Guava LocalCache 缓存介绍及实现源码深入剖析
guava LocalCache与ConcurrentHashMap有以下不同
- ConcurrentHashMap ”分段控制并发“是隐式的(实现中没有Segment对象),而LocalCache 是显式的。在jdk1.8 之后,ConcurrentHashMap采用synchronized+CAS 实现:当put的元素在哈希桶数组中不存在时,直接CAS进行写操作;在发生哈希冲突的情况下使用synchronized锁定头节点。其实是比分段锁更细粒度的锁实现,只在特定场景下锁定其中一个哈希桶,降低锁的影响范围。
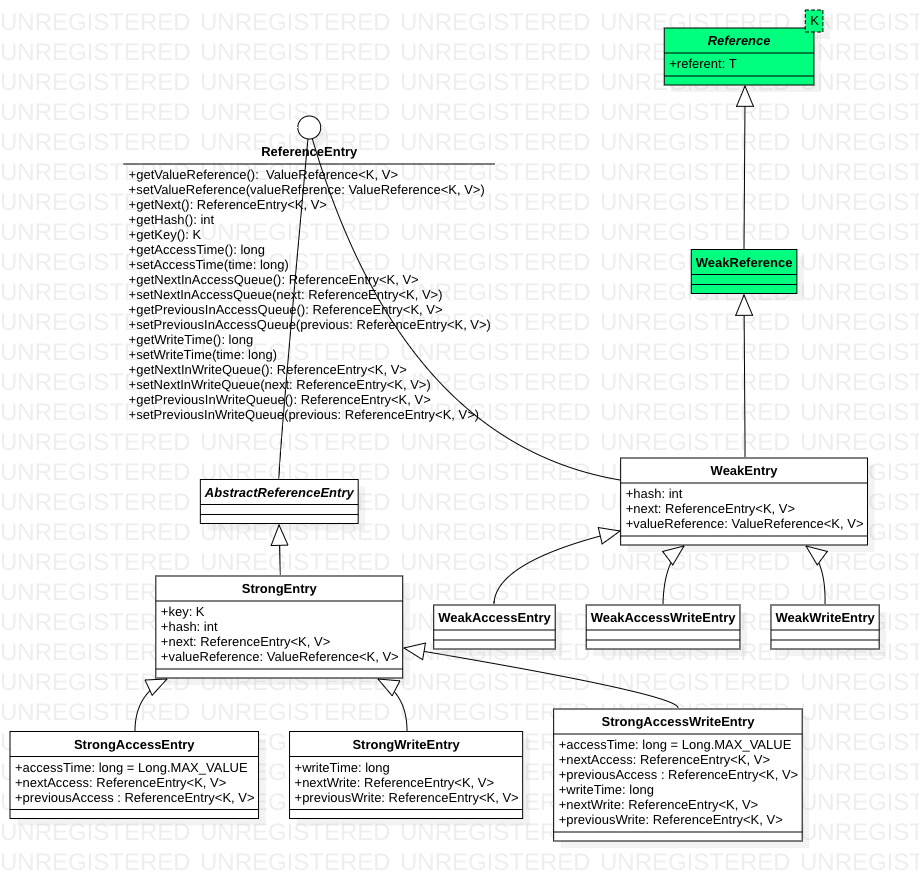
- 在Cache中,使用ReferenceEntry来封装键值对,并且对于值来说,还额外实现了ValueReference引用对象来封装对应Value对象。
- 在Cache 中支持过期 + 自动loader机制,这也使得其加锁方式与ConcurrentHashMap 不同。
- 在Cache中,在segment 粒度上支持了LRU机制, 体现在Segment上就是 writeQueue 和 accessQueue。队列中的元素按照访问或者写时间排序,新的元素会被添加到队列尾部。如果,在队列中已经存在了该元素,则会先delete掉,然后再尾部add该节点

- 我们一般用的LoadingCache 实际实现类是 LocalLoadingCache,LocalLoadingCache 封装了LocalCache ==> 整个guava cache的核心是LocalCache。
- AbstractCache:This class provides a skeletal implementation of the Cache interface to minimize the effort required to implement this interface.To implement a cache, the programmer needs only to extend this class and provide an implementation for the
get(Object)andgetIfPresentmethods.
LocalCache 的核心是Segment
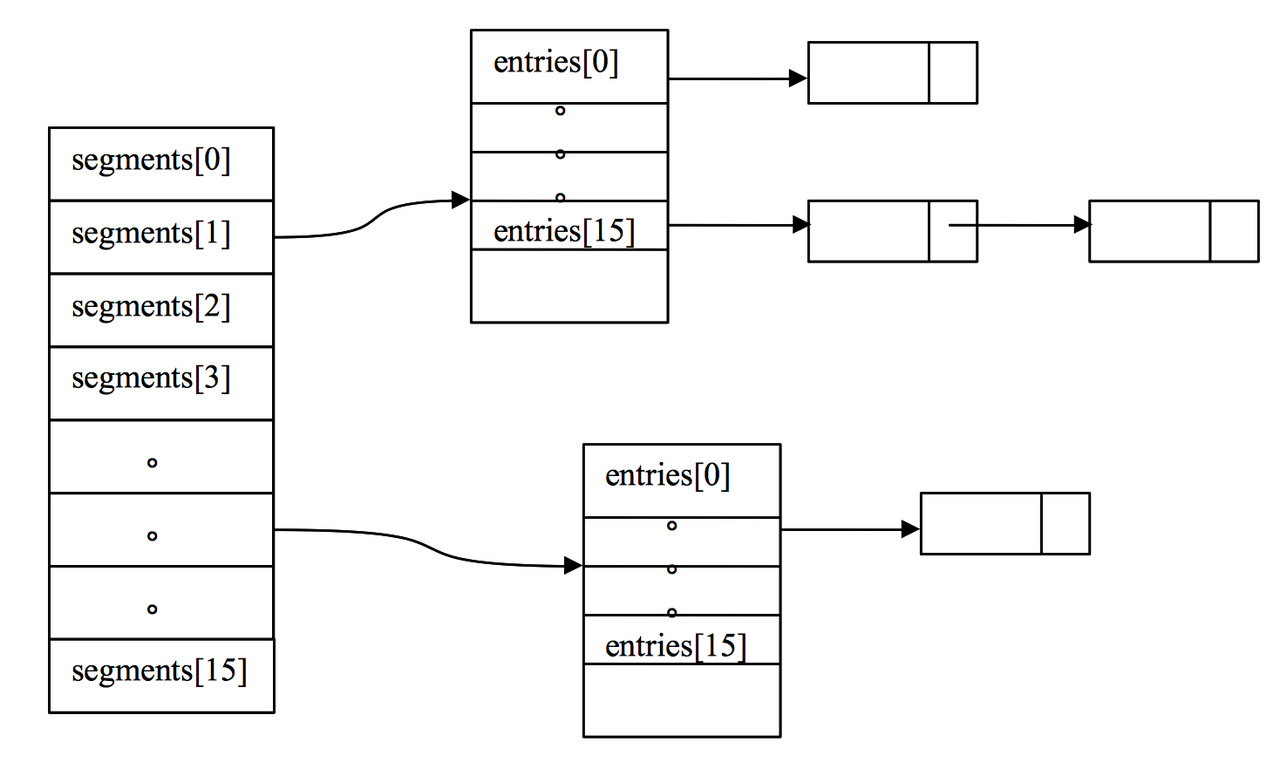
可以直观看到cache是以segment粒度来控制并发get和put等操作的
Segment 核心是ReferenceArray 和 ValueReference
static class Segment<K, V> extends ReentrantLock {
volatile @MonotonicNonNull AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table;
V get(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = getEntry(key, hash);
// fast path
if (e != null) {
V value = getLiveValue(e, now);
if (value != null) {
return xx // 找到值则直接返回
}
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
if (valueReference.isLoading()) { // 如果正在加载则进入等待
return waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference);
}
}
// slow path 进入load 逻辑
return lockedGetOrLoad(key, hash, loader); // ==> loadingValueReference.loadFuture
}
V waitForLoadingValue(ReferenceEntry<K, V> e, K key, ValueReference<K, V> valueReference)
throws ExecutionException {
...
V value = valueReference.waitForValue(); // LoadingValueReference.waitForValue ==> future.get
...
}
}
为了减少不必要的load加载,在ValueReference中(而不是常规的在key 上加锁)增加了loading标识和wait方法等待加载获取值。这样,调用方线程就可以等待上一个线程loader方法获取值,而不是重复去调用loader方法加重系统负担,而且可以更快的获取对应的值。
请求合并的实现
所谓请求合并:当多个线程请求同一个key时,第一个线程执行loader逻辑,其余线程等待。
主要逻辑就两个:lockedGetOrLoad 和 waitForLoadingValue

干活线程 segment.get.lockedGetOrLoad
对于当前线程,如果没有发现其它线程加载,则开始load 逻辑
V lockedGetOrLoad(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e;
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = null;
LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference = null;
boolean createNewEntry = true;
lock(); // 加锁
int newCount = this.count - 1;
AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table;
// 计算key在数组中的落点
int index = hash & (table.length() - 1);
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = table.get(index);
// 沿着某个index 链表依次遍历
for (e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) {
K entryKey = e.getKey();
if (e.getHash() == hash
&& entryKey != null
&& map.keyEquivalence.equivalent(key, entryKey)) {
valueReference = e.getValueReference();
V value = valueReference.get();
if (value == null || map.isExpired(e, now){
enqueueNotification(...);
} else {
return value;
}
this.count = newCount; // write-volatile
break;
}
}
loadingValueReference = new LoadingValueReference<>();
if (e == null) {
e = newEntry(key, hash, first);
e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference);
table.set(index, e);
} else {
e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference);
}
unlock(); // 解锁
synchronized (e) {
return loadSync(key, hash,loadingValueReference, loader);
}
}
segment 简单说也是数组加链表,只是元素类型是ReferenceEntry,
- 根据key 找到对应的ReferenceEntry
- 判断ReferenceEntry.getValueReference 中的 value元素是否有效,若有效则直接返回,
- 若无效(null or 过期)则创建loadingValueReference 并更新到 key 的ReferenceEntry。
- load逻辑 转给 loadingValueReference.loadFuture 执行
只有ReferenceEntry 更新 其value引用 loadingValueReference 的部分是需要加锁的,之后线程竞争便转移到了 loadingValueReference 上
V loadSync(K key,int hash,
LoadingValueReference<K, V>,loadingValueReference,CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader)throws ExecutionException {
ListenableFuture<V> loadingFuture = loadingValueReference.loadFuture(key, loader);
return getAndRecordStats(key, hash,loadingValueReference, loadingFuture);
}
public ListenableFuture<V> loadFuture(K key, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
...
V newValue = loader.load(key);
return set(newValue) ? futureValue : Futures.immediateFuture(newValue);
...
}
等待线程等待逻辑/waitForLoadingValue
LoadingValueReference 中包含loading 信息,相对于被包裹的Value 而言,类似于jvm中 object 对象头mark word,线程发现value 处于loading状态时 便直接 LoadingValueReference.waitForValue ==> future.get 准备等结果了。
V waitForLoadingValue(ReferenceEntry<K, V> e, K key, ValueReference<K, V> valueReference)
throws ExecutionException {
checkState(!Thread.holdsLock(e), "Recursive load of: %s", key);
V value = valueReference.waitForValue();
if (value == null) {
throw new InvalidCacheLoadException("CacheLoader returned null for key " + key + ".");
}
...
return value;
}
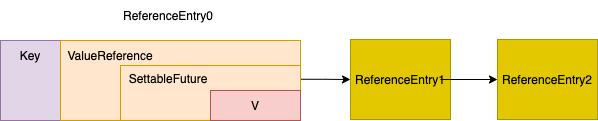
static class LoadingValueReference<K, V> implements ValueReference<K, V> {
volatile ValueReference<K, V> oldValue;
final SettableFuture<V> futureValue =SettableFuture.create();
final Stopwatch stopwatch =Stopwatch.createUnstarted();
public boolean set(@Nullable V newValue) {
return futureValue.set(newValue);
}
public V get() {
return oldValue.get();
}
public V waitForValue() throws ExecutionException {
// 对future.get的封装
return getUninterruptibly(futureValue);
}
public boolean setException(Throwable t) {
return futureValue.setException(t);
}
public void notifyNewValue(@Nullable V newValue) {
if (newValue != null) {
// future.get ==> waitForValue即可立即返回
set(newValue);
} else {
oldValue = unset();
}
}
}
从上述代码可以看到,LoadingValueReference 持有了 SettingFuture对象,干活线程 通过SettingFuture setValue, 等待线程 通过SettingFuture getValue。
与key 作为竞争点对比(线程竞争key的 访问权)
- 以 key 或者value 作为竞争点 + lock/unlock,线程发现key 数据过期,锁住key(标识key等手段),获取数据,解锁key。因为你不知道key/value 什么时候过期,所以每次lock/unlock 是很大的浪费。
- 以 value isLoading 作为竞争点,线程发现value isNotLoading,创建一个新的value 对象设置状态为loading,原子的修改entry的value,这样其它线程可以根据loading 状态决定自己的行为,而不是无脑lock/unlock
如果不想线程排队
Guava Cache内存缓存使用实践-定时异步刷新及简单抽象封装
Guava Cache 原理分析与最佳实践为什么这个方案解了 “缓存击穿” 问题但又没完全解?大量的线程阻塞导致线程无法释放,甚至会出现线程池满的尴尬场景。比较合适的方式是通过添加一个异步线程池异步刷新数据,所有请求线程直接返回老值(业务线程不会阻塞),同时对于 DB 的访问的流量可以被后台线程池的池大小控住。
只有一个用户线程排队
refreshAfterWrite 注意不是 expireAfterWrite
如果缓存过期,恰好有多个线程读取同一个key的值,那么guava只允许一个线程去加载数据,其余线程阻塞。这虽然可以防止大量请求穿透缓存,但是效率低下。使用refreshAfterWrite可以做到:只阻塞加载数据的线程,其余线程返回旧数据。
LoadingCache<String, Object> caches = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.refreshAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build(new CacheLoader<String, Object>() {
@Override
public Object load(String key) throws Exception {
return generateValueByKey(key);
}
});
另起线程拉新值
真正加载数据的那个线程一定会阻塞,可以让这个加载过程是异步的,这样就可以让所有线程立马返回旧值
ListeningExecutorService backgroundRefreshPools = MoreExecutors.listeningDecorator(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20)); LoadingCache<String, Object> caches = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100)
.refreshAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.build(new CacheLoader<String, Object>() {
@Override
public Object load(String key) throws Exception {
return generateValueByKey(key);
}
@Override
public ListenableFuture<Object> reload(String key, Object oldValue) throws Exception {
return backgroundRefreshPools.submit(new Callable<Object>() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
return generateValueByKey(key);
}
});
}
});
其它
弱引用
| 回收时机 | |
|---|---|
| Strong Reference | 若一个对象通过一系列强引用可到达,它就是强可达的(strongly reachable),那么它就不被回收 |
| Soft Reference | 在内存不充足时才会被回收 |
| Weak Reference | gc时 |
| Phantom Reference/虚引用 | 通过虚引用甚至无法获取到被引用的对象 |
垃圾收集器会把那些刚清除的弱引用放入创建弱引用对象时所指定的引用队列(Reference Queue)中
Product productA = new Product(...);
WeakReference<Product> weakProductA = new WeakReference<>(productA);
当productA变为null时(表明它所引用的Product已经无需存在于内存中),这时指向这个Product对象的就只剩弱引用对象weakProductA了,这时候相应的Product对象是弱可达的。
在Cache分别实现了基于Strong,Soft,Weak三种形式的ValueReference实现。
- 这里ValueReference之所以要有对ReferenceEntry的引用是因为在WeakReference、SoftReference被回收时,需要使用其key将对应的项从Segment段中移除;
- copyFor()函数的存在是因为在expand(rehash)重新创建节点时,对WeakReference、SoftReference需要重新创建实例(C++中的深度复制思想,就是为了保持对象状态不会相互影响),而对强引用来说,直接使用原来的值即可,这里很好的展示了对彼变化的封装思想;
- notifiyNewValue只用于LoadingValueReference,它的存在是为了对LoadingValueReference来说能更加及时的得到CacheLoader加载的值。
segment 类图

Map类结构简单说就是数组 + 链表,最基本的数据单元是entry