简介
ansible 基于python 开发
Ansible只需要在一台普通的服务器上运行即可(无需setup),不需要在被管控的服务器上安装客户端(Agentless )。运行Ansible的服务器这里俗称“管理节点”;通过Ansible进行管理的服务器俗称“受控节点”。
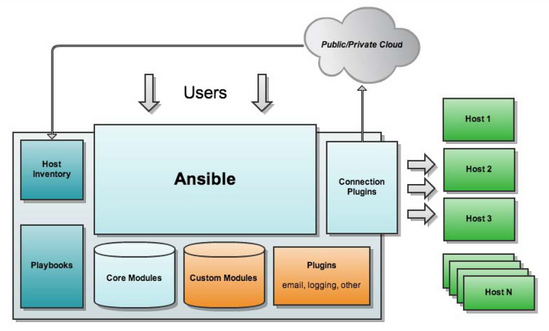
- Host Inventory:定义ansible管理的主机,可以进行分组管理。Ansible represents what machines it manages using a very simple INI file that puts all of your managed machines in groups of your own choosing.
- Playbooks:剧本或编辑是Ansible的任务配置文件、将多个任务定义在剧本中由Ansible自动执行,Playbooks最大的好处就是支持幂等,也就是说相同的任务不管执行多少次其结果是不变的,带来的好处也就是持续可维护性。
这两个描述了 我们比较关心的:让who 干what
来个sample 找找感觉
inventory文件,默认使用/etc/ansible/hosts,对于自定义 inventory 文件 custom_inventory,要加 -i 参数
[demo]
192.168.1.1
[test]
192.168.1.2
执行 ansible -i custom_inventory test -m ping,ping 是ansible 的一个特定模块,用来测试 “管理节点” 对“受控节点” 是否是通的。不推荐使用命令行的方式操作ansible ,此处只为demo 示例
module
尽量使用Modules替代Run Commands
Fabric直接通过SSH运行命令,Ansible先将Module(就是一段programs)推送到目标服务器,再远程执行。 Ansible works by connecting to your nodes and pushing out small programs, called “Ansible modules” to them. These programs are written to be resource models of the desired state of the system. Ansible then executes these modules (over SSH by default), and removes them when finished. 所有ansible 中干活儿都跟 module 有关系。
- 推荐使用yaml 而不是直接使用 命令。类似于kubectl 不推荐使用
kubectl run一样。 allow you to describe your automation jobs in a way that approaches plain English. - Think declaratively - Ansible is a desired state engine by design, do not “write code”。描述期望状态,而不是动作指令。理念是很先进的,但带来了一定的学习成本
比如安装一个应用,yum install httpd 不如
- hosts: web
name: installs and starts apache
tasks:
- name: install apache packages
yum:
name: httpd
state: latest
移除一个文件 rm file 不如if [ -f foo ];then rm foo;fi 不如 使用file module
- file:
path: foo
state: absent
也就是,确保 foo 文件是absent ,而不是每次执行 rm 执行
常用模块
ansible-doc -l查看所有模块,可以使用ansible-doc -s module来查看某个模块的参数,也可以使用ansible-doc help module来查看该模块更详细的信息
ansible playbook模式及语法
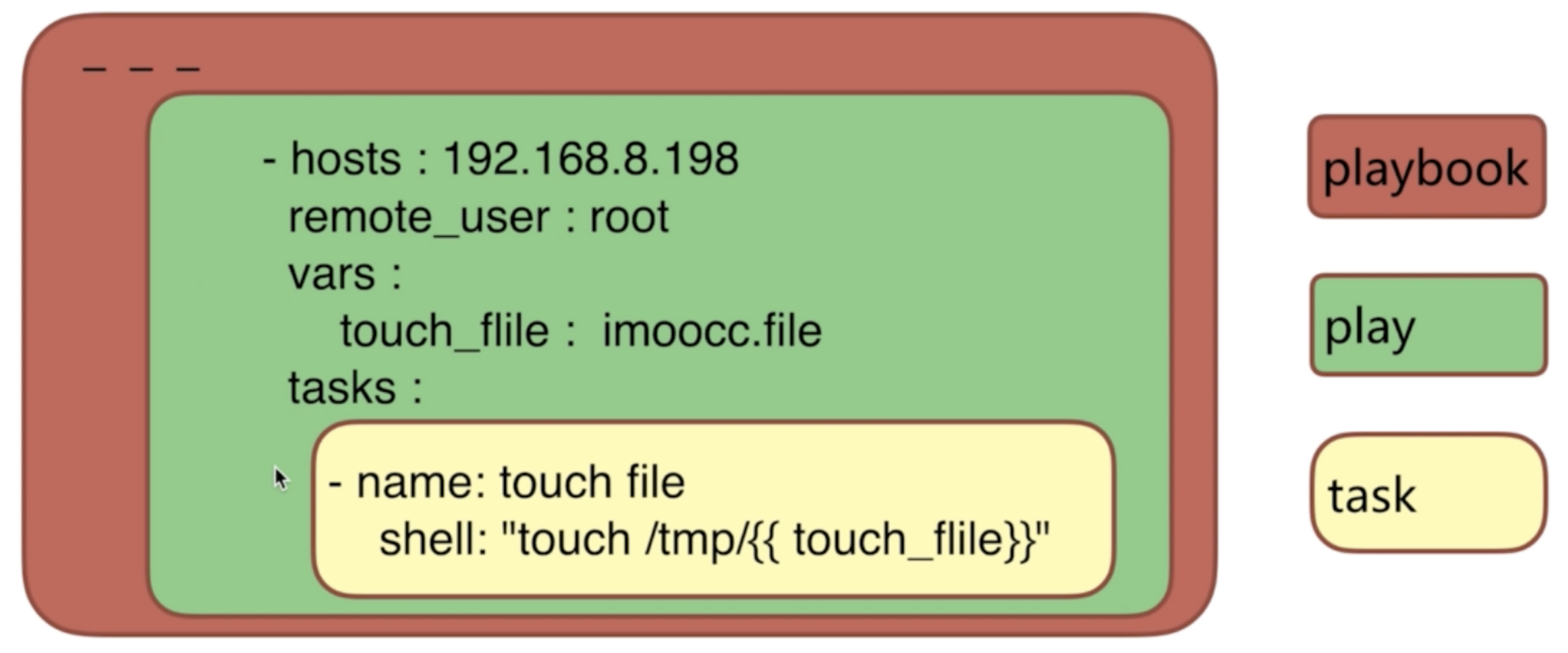
ansible playbook模式及语法 playbook 翻译过来就是”剧本”
Playbooks contain plays
Plays contain tasks
Tasks call modules
Tasks run sequentially
Handlers are triggered by tasks,
and are run once, at the end of play
role
当我们刚开始学习运用playbook时,可能会把playbook写成一个很大的文件,到后来可能你会希望这些文件是可以方便去重用的,所以需要重新去组织这些文件。
- 使用include语句引用task文件的方法,可允许你将一个配置策略分解到更小的文件中。
- 若 include 的文件 依赖一些变量,或者依赖文件本身很大,则需要include 多个文件
- roles就是通过分别将变量、文件、任务、模块及处理器放置于单独的目录中,引用这个目录就相当于include 所有文件了
Roles are ways of automatically loading certain vars_files, tasks, and handlers based on a known file structure.
Role Directory Structure
role通过使用约定的目录结构来存储playbook中的各个元素,例子
site.yml
webservers.yml
fooservers.yml
roles/
common/
tasks/
handlers/
files/
templates/
vars/
defaults/
meta/
webservers/
tasks/
defaults/
meta/
- tasks - contains the main list of tasks to be executed by the role.
- handlers - contains handlers, which may be used by this role or even anywhere outside this role.
- defaults - default variables for the role (see Using Variables for more information).
- vars - other variables for the role (see Using Variables for more information).
- files - contains files which can be deployed via this role.
- templates - contains templates which can be deployed via this role.
- meta - defines some meta data for this role.
Using Roles
- hosts: webservers
roles:
- common
- webservers
handler
这个概念入门时可以先忽略
The easiest way to think about Handlers is that they are fancy Tasks.
首先,你可以理解为 handler 和 task 一样,然后再理解他们之间的差异
| 触发 语法 | 一定执行么 | |
|---|---|---|
| task | 写在 yaml 中就会被触发 | yaml 执行就会被执行 |
| hanlder | We call Handlers using the notify syntax. | 上游的task 真正执行了,才会被触发 |
小结
本文思路
- ansible 整体,本质就两个:在哪个主机上干什么活儿
- 上面这个事情由一个剧本来描述
- 剧本太长了 怎么分章节
写自动化脚本的目的是让目标主机达到所需的状态,而不仅仅是机械的执行一连串命令,Ansible就是以这样的理念来设计的,大部分module都会由当前状态来判断是否需要执行,因此module的执行是幂等的,此外每一个task都有一个changed状态,来表示这次运行是否对目标主机产生了改变,没有改变就不要去fix,像handler只会在task的changed == true时才会被执行。这也是为什么我们写task时应该尽量使用相应的module,而少用run commands例如shell的原因,因为Ansible无法判断shell运行内容,因此changed永远为true,此外大部分的shell命令都不是幂等的,重复执行结果无法预期。